statmark
Plots a set of markers based on a combination (typically the mean) of input array-valued coordinates. The input X and Y coordinates must be fixed-length arrays of length N; N markers are plotted, each one representing the mean (or median, minimum, maximum, ...) of all the input array elements at the corresponding position.
Note that because the X and Y arrays must be of a fixed size for all rows, and because combination is performed in both X and Y directions, this is typically only suitable for plotting combined spectra if they all share a common horizontal axis, e.g. are all sampled into the same wavelength bins. To visually combine spectra with non-uniform sampling, the arrayquantile plotter may be more useful.
Usage Overview:
layerN=statmark xcombineN=mean|median|min|max|q.01|...
ycombineN=mean|median|min|max|q.01|...
colorN=<rrggbb>|red|blue|...
shapeN=filled_circle|open_circle|... sizeN=<pixels>
xsN=<array-expr> ysN=<array-expr> inN=<table>
ifmtN=<in-format> istreamN=true|false icmdN=<cmds>
All the parameters listed here
affect only the relevant layer,
identified by the suffix
N.
Example:

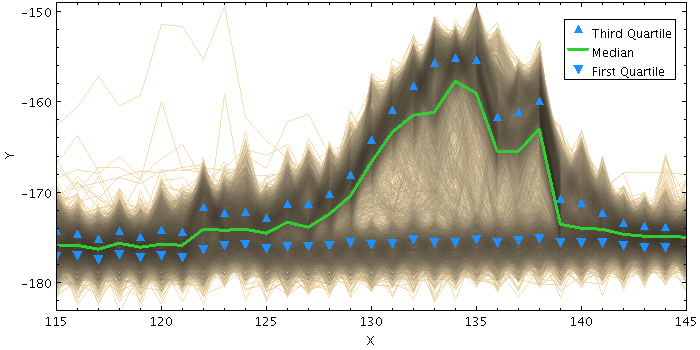
stilts plot2plane in=LRS_NPW_V010_20071101.cdf ys=RX1
xmin=115 xmax=145 ymin=-183 ymax=-149 xpix=700 xcrowd=0.8
layer-d=lines color-d=wheat
layer-m=statline ycombine-m=median color-m=LimeGreen thick-m=3
color-q=DodgerBlue size-q=4
layer-q1=statmark ycombine-q1=Q1 shape-q1=filled_triangle_up
layer-q3=statmark ycombine-q3=Q3 shape-q3=filled_triangle_down
leglabel-m=Median leglabel-q1='First Quartile' leglabel-q3='Third Quartile'
legseq=-q3,-m,-q1 legpos=0.98,0.93
colorN = <rrggbb>|red|blue|... (Color)
The standard plotting colour names are
red, blue, green, grey, magenta, cyan, orange, pink, yellow, black, light_grey, white.
However, many other common colour names (too many to list here)
are also understood.
The list currently contains those colour names understood
by most web browsers,
from AliceBlue to YellowGreen,
listed e.g. in the
Extended color keywords section of
the CSS3 standard.
Alternatively, a six-digit hexadecimal number RRGGBB
may be supplied,
optionally prefixed by "#" or "0x",
giving red, green and blue intensities,
e.g. "ff00ff", "#ff00ff"
or "0xff00ff" for magenta.
[Default: red]
icmdN = <cmds> (ProcessingStep[])
inN.
The value of this parameter is one or more of the filter
commands described in Section 6.1.
If more than one is given, they must be separated by
semicolon characters (";").
This parameter can be repeated multiple times on the same
command line to build up a list of processing steps.
The sequence of commands given in this way
defines the processing pipeline which is performed on the table.
Commands may alternatively be supplied in an external file,
by using the indirection character '@'.
Thus a value of "@filename"
causes the file filename to be read for a list
of filter commands to execute. The commands in the file
may be separated by newline characters and/or semicolons,
and lines which are blank or which start with a
'#' character are ignored.
A backslash character '\' at the end of a line
joins it with the following line.
ifmtN = <in-format> (String)
inN.
The known formats are listed in Section 5.1.1.
This flag can be used if you know what format your
table is in.
If it has the special value
(auto) (the default),
then an attempt will be
made to detect the format of the table automatically.
This cannot always be done correctly however, in which case
the program will exit with an error explaining which
formats were attempted.
This parameter is ignored for scheme-specified tables.
[Default: (auto)]
inN = <table> (StarTable)
-",
meaning standard input.
In this case the input format must be given explicitly
using the ifmtN
parameter.
Note that not all formats can be streamed in this way.:<scheme-name>:<scheme-args>.<" character at the start,
or a "|" character at the end
("<syscmd" or
"syscmd|").
This executes the given pipeline and reads from its
standard output.
This will probably only work on unix-like systems.istreamN = true|false (Boolean)
inN parameter
will be read as a stream.
It is necessary to give the
ifmtN parameter
in this case.
Depending on the required operations and processing mode,
this may cause the read to fail (sometimes it is necessary
to read the table more than once).
It is not normally necessary to set this flag;
in most cases the data will be streamed automatically
if that is the best thing to do.
However it can sometimes result in less resource usage when
processing large files in certain formats (such as VOTable).
This parameter is ignored for scheme-specified tables.
[Default: false]
shapeN = filled_circle|open_circle|... (MarkerShape)
The available options are:
filled_circle
open_circle
cross
x
open_square
open_diamond
open_triangle_up
open_triangle_down
fat_circle
fat_cross
fat_x
fat_square
fat_diamond
fat_triangle_up
fat_triangle_down
filled_square
filled_diamond
filled_triangle_up
filled_triangle_down
[Default: filled_circle]
sizeN = <pixels> (Integer)
[Default: 4]
xcombineN = mean|median|min|max|q.01|... (Combiner)
The available options are:
mean: the mean of the combined valuesmedian: the medianmin: the minimum of all the combined valuesmax: the maximum of all the combined valuesq.01: 1st percentileq1: first quartileq3: third quartileq.99: 99th percentilestdev: the sample standard deviation of the combined valuessum: the sum of all the combined values per bincount: the number of non-blank values per bin (weight is ignored)[Default: mean]
xsN = <array-expr> (String)
The value is an array-valued algebraic expression based on column names as described in Section 10. Some of the functions in the Arrays class may be useful here.
ycombineN = mean|median|min|max|q.01|... (Combiner)
The available options are:
mean: the mean of the combined valuesmedian: the medianmin: the minimum of all the combined valuesmax: the maximum of all the combined valuesq.01: 1st percentileq1: first quartileq3: third quartileq.99: 99th percentilestdev: the sample standard deviation of the combined valuessum: the sum of all the combined values per bincount: the number of non-blank values per bin (weight is ignored)[Default: mean]
ysN = <array-expr> (String)
The value is an array-valued algebraic expression based on column names as described in Section 10. Some of the functions in the Arrays class may be useful here.