Next Previous Up Contents
Next: Old-Style Plot Windows
Up: Time Plot Window
Previous: Time Navigation
Note: the Time Plot has multiple plot
Zones,
and the axes are configured individually for each zone.
The Axes ( ) control for the
time plot window has the following tabs:
) control for the
time plot window has the following tabs:
Coords Tab
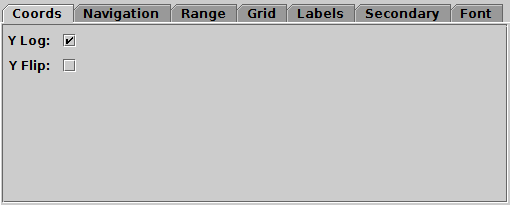
Coords tab of time Axes control
The Coords tab controls the vertical axis coordinates
(you can't flip or rescale the time axis).
It has the following options:
-
Y Scale
- Selects scaling (linear, log, asinh, symlog) for the Y axis.
See Appendix A.4.2.4.
-
Y Flip
- If selected, vertical axis coordinate axes increase down rather
than up.
Navigation Tab
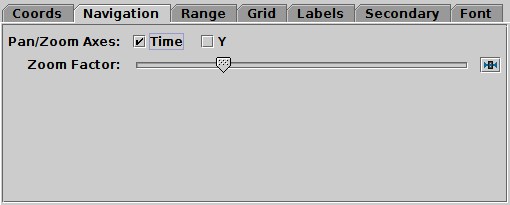
Navigation tab of time Axes control
The Navigation tab controls details of how the
navigation works.
It has the following options:
-
Pan/Zoom Axes
- By default, dragging with the mouse or using the mouse wheel
on the body of the plot
will pan or zoom in the horizontal (time) direction only,
which is usually what you want for a time series.
Using this control you can make it work in the vertical direction as well.
-
Zoom Factor
- Controls the factor by which each zoom action zooms the plot.
Moving this slider to the left/right makes the mouse more/less sensitive
(one wheel click or dragging a fixed distance has more/less zoom effect).
Range Tab
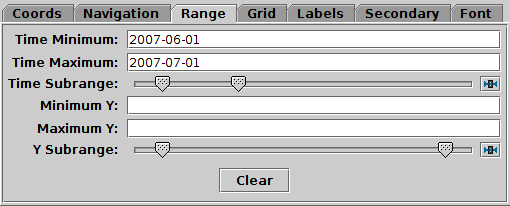
Range tab of time Axes control
The Range tab provides manual configuration of the
visible range of the plot. Making changes to this tab will reset
the visible plot range, but not vice versa - zooming and panning
in the usual way will not change the settings of this panel.
Filling in the Minimum/Maximum
fields for either or both axes will
constrain the corresponding range of the visible data.
The limits corresponding to any of those fields that are left blank
will initially be worked out from the data.
The Subrange double-sliders restrict the ranges
within the (explicit or automatic) min/max ranges.
Note you can move both sliders at once by grabbing a position between the two.
For the time axis, the range may be entered as an ISO-8601 date/time value.
The Clear button resets all the fields.
Grid Tab
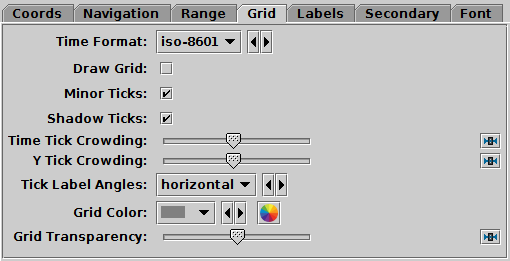
Grid tab of time Axes control
The Grid tab configures the appearance of the axis grid.
It has the following options:
-
Time Format
- Selects the representation for time/date in which the horizontal
axis is labelled.
Options are
ISO-8601,
decimal year,
Modified Julian Day,
and Unix (seconds since midnight on 1 Jan 1970).
-
Draw Grid
- If true, grid lines will be drawn across the plot
for every tick mark.
-
Minor Ticks
- If set, minor (unlabelled) tick marks will be drawn between the
major (labelled) ones.
-
Shadow Ticks
- If set and no secondary axis is in use, then tick marks without
numeric labels are painted along the axis opposite to the primary axis,
so that tick marks are visible along all edges not just the ones
with numeric labels.
If a secondary axis is in use, this setting is ignored.
-
Time/Y Tick Crowding
- Use the slider to influence how many tick marks are drawn on each axis.
-
Tick Label Angles
- Controls orientation of numeric labels on the axes.
By default they are drawn with horizontal alignment,
but you can also choose angled.
If adaptive is selected, they will be horizontal where
possible, but may be angled to accommodate more labels if
crowding is high;
note this option is currently not perfect
and can result in suboptimal border placement.
-
Grid Colour
- Selects the colour with which grid lines will be drawn.
-
Grid Transparency
- Controls the transparency of the grid lines,
which are drawn over the plot content.
Labels Tab
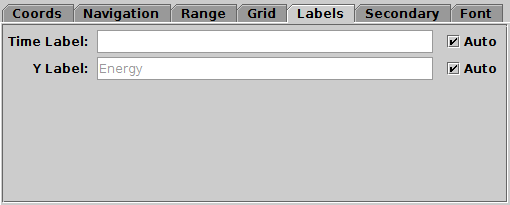
Labels tab of time Axes control
The Labels tab controls the text labels
on the horizontal and vertical axes.
If the Auto checkboxes are set,
the Time axis will be unlabelled,
and the Y axis label will be taken
from one of the data coordinates being plotted on the Y axis.
To override those with your own axis labels, unset Auto and type
text in to the field.
Secondary Axes Tab
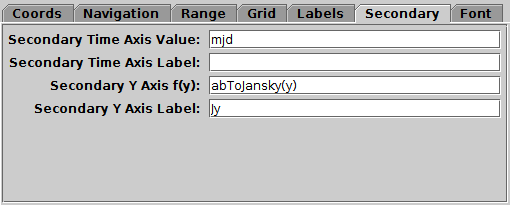
Secondary tab of time Axes control
The Secondary tab controls optional secondary
Time and Y axes at the top and right edges of the plot,
to go with the standard (primary) Time and Y axes at the bottom and left edges,
so for instance you can annotate the vertical dimension
with both magnitudes and flux,
or the horizontal dimension with both decimal year and MJD.
-
Secondary Time Axis Value
- Defines the secondary axis in relation to the time value displayed
on the primary one.
The value you enter is an algebraic expression
using one of the following variables:
-
mjd: Modified Julian Date
-
jd: Julian Day
-
decYear: decimal year CE
-
unixSec: seconds since 1970-01-01T00:00:00
In most cases, you will just use one of these strings, e.g.
"mjd" to label using MJD, but you can apply operations to these values
in the usual way if required, for instance to provide a differently offset
date scale.
The function supplied should be monotonic and reasonably well-behaved,
otherwise the secondary axis annotation may not work well. Tick marks
will always be applied on a linear scale. Currently there is no way to
annotate the secondary axis with ISO-8601 dates or other non-numeric
labels.
-
Secondary Time Axis Label
- Provides a textual annotation near the secondary Time axis
(at the top).
This can be supplied whether or not the Time axis mapping function
is actually present.
-
Secondary Y Axis f(y)
- Defines the secondary Y axis in relation to the primary one
by means of a supplied function of the variable y
that maps primary to secondary axis values,
written using TOPCAT's expression language.
The function supplied should be monotonic and reasonably well-behaved,
otherwise the secondary axis annotation may not work well.
TOPCAT will attempt to make a sensible decision about whether to
use linear or logarithmic tick marks.
-
Secondary Y Axis Label
- Provides a textual annotation near the secondary Y axis (on the right).
This can be supplied whether or not the Y axis mapping function
is actually present.
Font Tab
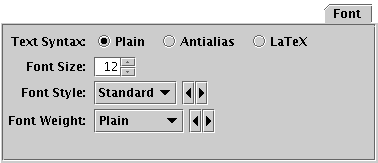
Font tab
The Font tab configures the font used for axis annotation.
It also affects some other things like the legend.
-
Text Syntax
- How to turn the text into characters on the screen.
Plain and Antialias both take the
text at face value, but Antialias smooths the characters.
Antialiased text usually looks nicer, but can be perceptibly slower to plot.
At time of writing, on MacOS antialiased text seems to be required to
stop the writing coming out upside-down for non-horizontal text.
LaTeX interprets the text as LaTeX source code
and typesets it accordingly.
-
Font Size
- Size of the font in points.
-
Font Style
- Style of the font.
-
Font Weight
- Whether the font is plain, bold or italic.
Next Previous Up Contents
Next: Old-Style Plot Windows
Up: Time Plot Window
Previous: Time Navigation
TOPCAT - Tool for OPerations on Catalogues And Tables
Starlink User Note253
TOPCAT web page:
http://www.starlink.ac.uk/topcat/
Author email:
m.b.taylor@bristol.ac.uk
Mailing list:
topcat-user@jiscmail.ac.uk
![]() ) control for the
time plot window has the following tabs:
) control for the
time plot window has the following tabs:






