Next Previous Up Contents
Next: 3D Plot Style Editor
Up: Old-Style Plot Windows
Previous: Lines Style Editor
This section describes an old-style plotting window.
The standard plotting windows are described in Appendix A.4.
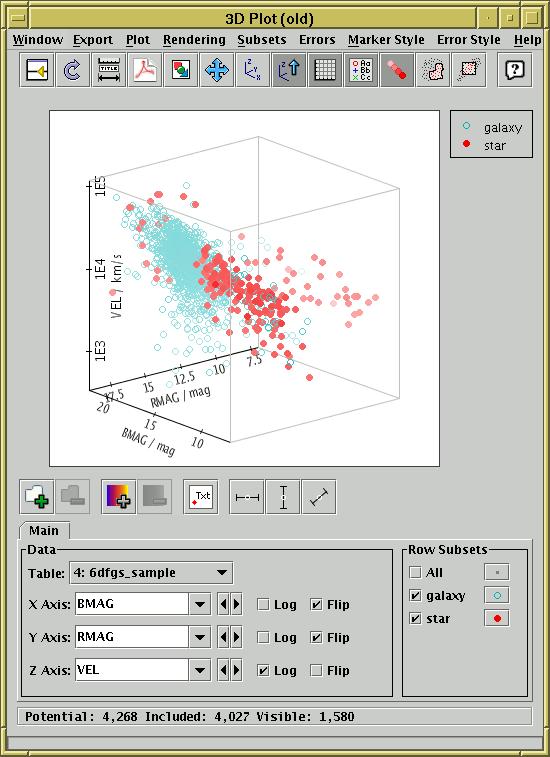
3D scatter plot window
The 3D plot window draws 3-dimensional scatter plots of one or more
triples of table columns (or derived quantities) on Cartesian axes.
You can display it using the 3D ( ) item
in the Control Window's
Graphics menu.
) item
in the Control Window's
Graphics menu.
On the display a marker is plotted for each row in the selected
dataset(s) at a position determined by the values in the table columns
selected to provide the X, Y and Z values.
A marker will only be plotted if none of the X, Y and Z values are blank.
Select the quantities to plot and the plotting symbols with the
dataset selector
at the bottom.
The 3D space can be rotated by dragging the mouse around on the
surface - it will rotate around the point in the centre of the
plotted cube. The axis labels try to display themselves the right
way up and in a way which is readable from the viewing point if possible,
which means they move around while the rotation is happening.
By default the points are rendered as though the 3D space is filled
with a 'fog', so that more distant points appear more washed out -
this provides a visual cue which can help to distinguish the depth
of plotted points. However, you can turn this off if you want.
If there are many points, then you may find that they're not all plotted
while a drag-to-rotate gesture is in progress. This is done to cut down on
rendering time so that GUI response stays fast. When the drag is
finished (i.e. when you release the mouse button) all the points will
come back again.
Zooming is also possible. You can zoom in around the
centre of the plot so that the viewing window only covers the middle.
The easiest way to do this is to use the mouse wheel if you have one -
wheel forward to zoom in and backward to zoom out.
Alternatively you can do it by dragging on the region to the left of
the plot, like the Axis Zoom in some of the 2-d plots.
Drag the mouse down to zoom in or up to zoom
out on this part of the window. Currently it is only possible
to zoom in/out around the centre of the plot.
When zoomed you can use the
Subset From Visible ( ) toolbar button
to define a new Row Subset consisting only of the
points which are currently visible.
See Appendix A.5.1.6 for more explanation.
) toolbar button
to define a new Row Subset consisting only of the
points which are currently visible.
See Appendix A.5.1.6 for more explanation.
Clicking on any of the plotted points will activate it -
see Section 8.
The following buttons are available on the toolbar:
-
 Split Window
Split Window
- Allows the dataset selector to be resized by dragging a separator
between it and the plot area. Good for small screens.
-
 Replot
Replot
- Redraws the current plot. It is usually not necessary to
use this button, since if you change any of the plot characteristics
with the controls in this window the plot will be redrawn
automatically. However if you have changed the data, e.g. by
editing cells in the Data Window,
the plot is not automatically redrawn (since this is potentially an
expensive operation and you may not require it).
Clicking this button redraws the plot taking account of any changes
to the table data.
-
 Configure Axes and Title
Configure Axes and Title
- Pops up a dialogue to allow manual configuration of axis ranges,
axis labels and plot title - see Appendix A.5.1.2.
-
 Export as PDF
Export as PDF
- Pops up a dialogue which will write the current plot as a PDF file.
In general this is a faithful and high quality rendering of what
is displayed in the plot window. However, if plotting is being done
using the transparent markers, the markers will
be rendered as if they were opaque.
Plots with very many points can result in rather large output PDFs.
-
 Export as GIF
Export as GIF
- Pops up a dialogue which will output the current plot to a GIF file.
The output file is just the same as the plotted image that you see.
Resize the plotting window before the export to control the size
of the output GIF.
-
 Rescale
Rescale
- Rescales the axes of the current plot so that it contains all
the data points in the currently selected subsets.
By default the plot will be scaled like this, but it it may have changed
because of changes in the subset selection.
-
 Reorient
Reorient
- Reorients the axes of the current plot to their default position.
This can be useful if you've lost track of where you've rotated
the plot to with the mouse. This also resets the zoom level to
normal if you've changed it.
-
 Stay Upright
Stay Upright
- Toggle button which when selected ensures that the Z axis is
oriented vertically on the screen at all times.
By default this is off which means you can drag the axes round to
any orientation, but it can be convenient to switch it on to keep
the plot pointing in a sensible direction.
-
 Grid
Grid
- Toggles whether the cubic frame bounding the plot is drawn or not.
-
 Show Legend
Show Legend
- Toggles whether a legend showing how each data set is represented
is visible to the right of the plot. Initially the legend is shown
only if more than one data set is being shown at once.
-
 Fog
Fog
- Toggles whether rendering is done as if the space is filled with fog.
If this option is selected, distant points will appear more washed out
than near ones.
-
 Draw Subset Region
Draw Subset Region
- Allows you to draw a region on the screen defining a new
Row Subset. When you have finished
drawing it, click this button again to indicate you're done.
The subset will include points at all depths in the viewing direction
which fall in the region you have drawn.
See Appendix A.5.1.6 for more details.
-
 Subset From Visible
Subset From Visible
- Defines a new Row Subset
consisting of only the points which
are currently visible on the plotting surface.
See Appendix A.5.1.6 for more explanation.
The following additional item is available as a menu item only:
-
 Antialias
Antialias
- Toggles whether the axes and their annotations are drawn antialiased.
Antialiased lines are smoother and generally look more pleasing,
especially for text at a sharp angle, but it can slow the rendering
down a bit.
The Dataset Toolbar contains the following options:
-
 /
/  Add/Remove dataset
Add/Remove dataset
- Adds/removes tabs in which the data for extra datasets can be entered.
See Appendix A.5.1.1.
-
 /
/  Add/Remove auxiliary axis
Add/Remove auxiliary axis
- Adds/removes a selector for entering an auxiliary axis to modify
point colours etc.
See Appendix A.5.1.5.
-
 Toggle point labelling
Toggle point labelling
- Allows text labels to be drawn near plotted points.
See Appendix A.5.1.4.
-
 /
/  /
/ 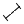 Toggle X/Y/Z error bars
Toggle X/Y/Z error bars
- Switches between drawing symmetric error bars and no error bars
in the X, Y and Z directions respectively.
Other options are available in the Errors menu.
See Appendix A.5.1.3.
You have considerable freedom to configure how the points are plotted
including the shape, colour and transparency of symbols and the
representation of error bars if used. These options are described
in the following subsection.
Next Previous Up Contents
Next: 3D Plot Style Editor
Up: Old-Style Plot Windows
Previous: Lines Style Editor
TOPCAT - Tool for OPerations on Catalogues And Tables
Starlink User Note253
TOPCAT web page:
http://www.starlink.ac.uk/topcat/
Author email:
m.b.taylor@bristol.ac.uk
Mailing list:
topcat-user@jiscmail.ac.uk


![]() ) item
in the Control Window's
Graphics menu.
) item
in the Control Window's
Graphics menu.
![]() ) toolbar button
to define a new Row Subset consisting only of the
points which are currently visible.
See Appendix A.5.1.6 for more explanation.
) toolbar button
to define a new Row Subset consisting only of the
points which are currently visible.
See Appendix A.5.1.6 for more explanation.